Overview
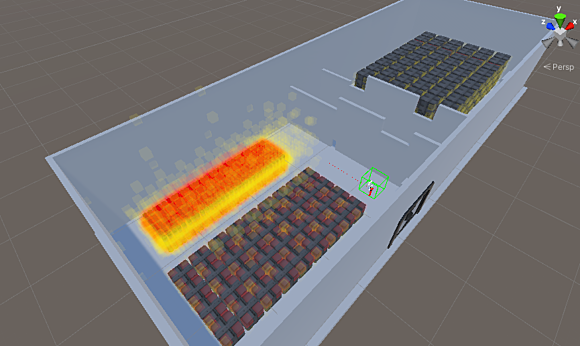
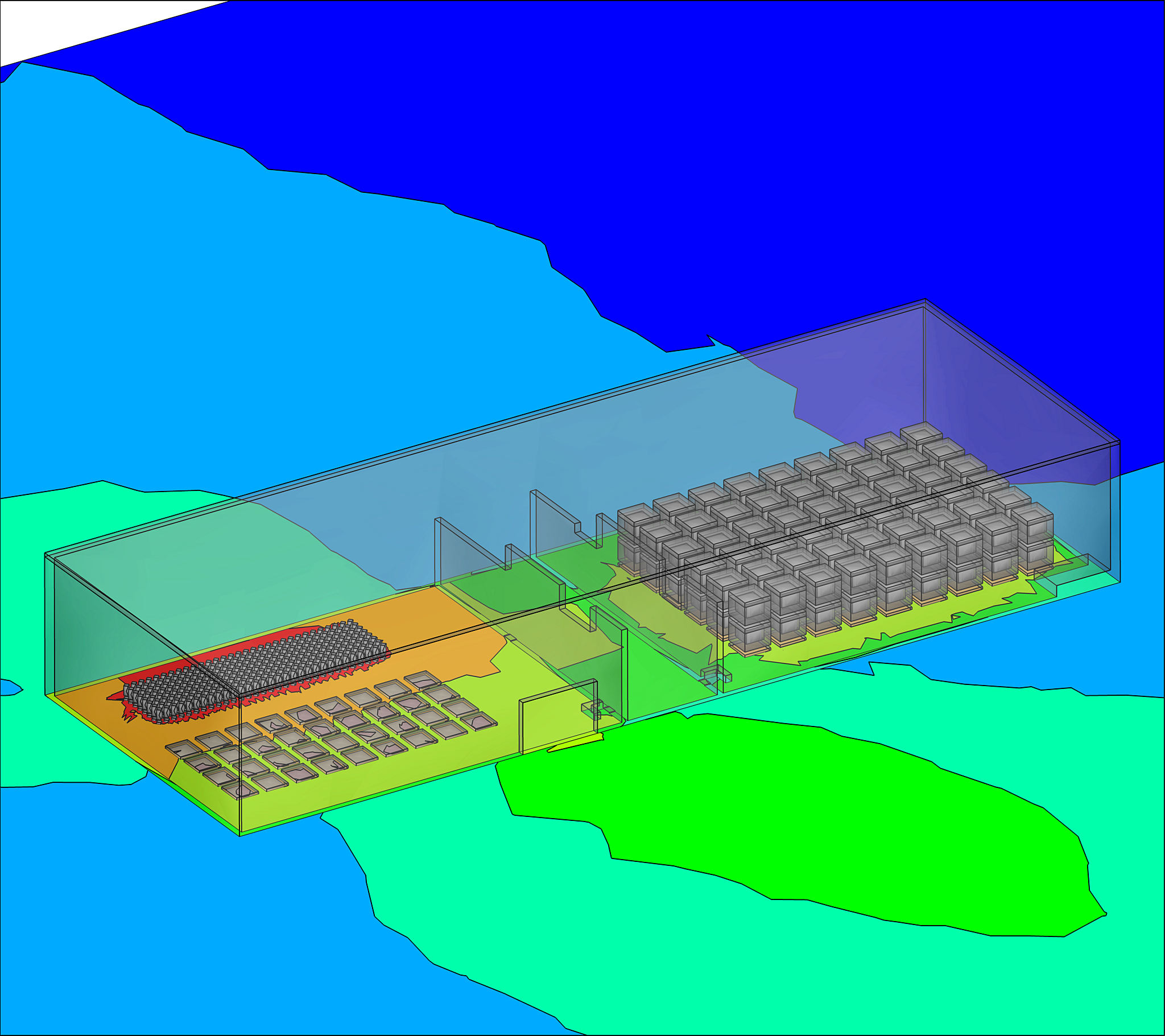
Radiation safety is a combination of safe practices and precautionary measures that are put in place to promote safety when working with or near radiation. The three primary means of minimizing radiation exposure are time, distance, and shielding. By calculating exposures to radiation in advance, it is possible to plan safer work practices and put preventive measures in place, so that worker exposure is minimized.
Shielding is a reliable way of reducing radiation exposure to workers. Barrier materials such as lead in the case of gamma radiation or water in the case of neutrons will block or reduce the radiation intensity and can significantly reduce worker exposure. The amount of shielding provided by any barrier will depend on the material and its thickness.
Our experienced shielding experts establish radiation exposure in various circumstances through calculation and advanced computer codes. In addition, our team leverages the decades of operational experience it has accumulated collaborating with nuclear clients to develop effective radiation safety plans and cost-effective approaches to shielding.
Why Us?
-
Highly Qualified Team
Our team includes physicists and nuclear engineers with extensive experience in nuclear power, nuclear medicine, isotope processing, containment, transportation, fuel fabrication, and waste management.
-
Wide Variety of Experience
We have worked on projects for waste management facilities, transport packages, shielded research facilities, fusion reactors, fission reactors, isotope production, and other specialized nuclear facilities.
-
Minimize Dose
Extensive experience enables us to quickly develop shielding designs, efficiently apply the right models, as well as develop approaches to projects that minimize dose.
-
Diverse Group of Experts
In-house experts in licensing, regulatory affairs, safety assessment, waste management, and decommissioning support our shielding activities and help us find the optimum solution.
Technical Abilities
Radiation Transport Software & Codes
We use advanced computer codes, such as Attila, Monte Carlo N-Particle transport code (MCNP) & Microshield, as well as analytical techniques, to support radiation transport calculations. This computer-assisted software is used to perform radiation shielding and dose modeling in support of shielding design and source strength estimation with the aim of minimizing exposure to individuals, in line with the As low As Reasonably Achievable (ALARA) principle.
The radiation shielding analysis software we use includes:
- MicroShield® – A point-kernel shielding analysis package used throughout the nuclear industry to analyze shielding for gamma radiation in standard geometries
- Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport (MCNP) – An extremely versatile Monte Carlo software package that can be used to analyze shielding for both gamma and neutron radiations in complex geometries
- ORIGEN – a computer code used to solve the equations of radioactive nuclide transmutation and calculate radiation source terms for use in shielding and dose rate calculations
- ATTILA - We have a collaboration with Silver Fir Software (https://silverfirsoftware.com/), the developers of the Attila suite of codes for the development of the code and its uses
- MACCS, ADDAM, and URI - Site & public dose assessments are calculated using these codes
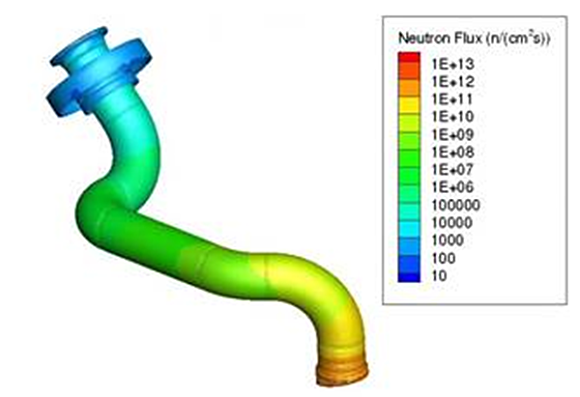
Applications
We have experience with a wide variety of analytical methods and radiation transport software that allow us to analyze problems including:
- Shielding calculations and assessment of shielding designs to support nuclear facilities and any other facility where radiation doses may be a concern
- Radiation from extended sources such as ground contamination and airborne plumes of radioactive material
- Generation of secondary radiation and activation analyses
- Support the preparation of Safety Analysis Reports (SAR), hazard assessments, ALARA assessments, etc.
- Calculation of radiation fields around nuclear facilities and contaminated sites and estimation of dose to workers and members of the public during normal and accidental/upset scenarios
- Provision of support to design engineers and the review of design packages
- Optimization of waste storage facilities
Knowledgeable Team
In addition to using state-of-the-art methods and computer codes to deliver services, personal solutions are provided by our experienced team that includes industry-recognized experts who are developing the latest standards pertaining to safety assessment and environmental management (for example, the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) N288 and N292 standards).
Our Proven Experience
Quality Assurance & Technical Standards
- 10CFR50 Appendix B (2021)
- Quality Assurance Criteria for Nuclear Power Plants and Fuel Reprocessing Plants
- ASME NQA-1 (2008)
- Quality Assurance Requirements for Nuclear Facility Applications
- CSA N286.7
- Quality assurance of analytical, scientific and design computer programs
- CSA N288
- Standards and Guidelines on Environmental Management of Nuclear Facilities
- CSA N292
- Standards on Radioactive Waste Management
- CSA N294
- Decommissioning of facilities containing nuclear substances
- CSA N299.1
- Quality Assurance Program Requirements for the Supply of Items and Services for nuclear power plants, Category 1